
- Advantages: high extinguishing efficiency, fast extinguishing speed, non-toxic, will not destroy the ozone layer, its equipment structure is simple, does not occupy or covers an area of small, easy to install, low cost.
- Extinguishing principle: gas-phase chemical inhibition, solid-phase chemical inhibition, reduction of oxygen concentration
- Hotline: 400-915-1190
Product Details
I. Principles of fire extinguishing
1, gas-phase chemical inhibition: under the action of heat, the decomposition of fire-fighting aerosols in the gasification of metal ions or loss of electrons in the cation can be burned with the active groups in the affinity reaction, repeated large consumption of the active groups, reducing the combustion of free radicals;
2, solid-phase chemical inhibition: fire-fighting aerosol particles in the particle size is very small (0.001 ~ 100μm), has a large surface area and surface energy, can be adsorbed in the combustion of reactive groups, and chemical action, a large number of consumption of reactive groups, reduce the combustion of free radicals;
3, reduce oxygen concentration: fire-fighting aerosol in the N2, CO2 can reduce the oxygen concentration in the combustion, but its speed is slow, fire-fighting role is much smaller than the heat absorption and cooling, chemical inhibition.
II. Main advantages
It has high extinguishing efficiency, fast extinguishing speed, non-toxic, will not destroy the ozone layer, and its equipment structure is simple, does not occupy or covers a small area, easy to install, low cost.
III. Existing types and specifications
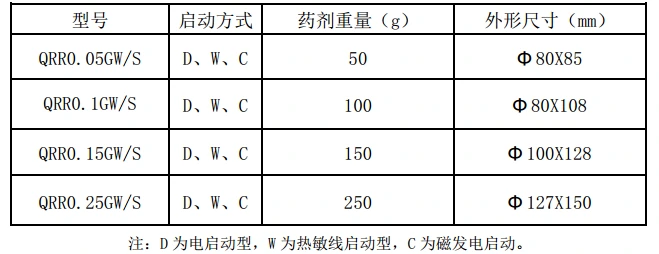
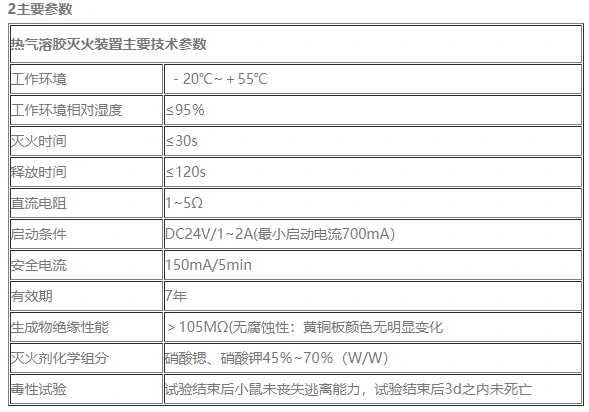
1 Main specifications
IV. Areas of application (places)
1, the main control system main control room, the central control room, the main electrical room, the communications center (including switch room, the main wiring room, power room, etc. of the program-controlled power station), the main operating room;
2. Transformer and distribution system (substation) - power distribution room, oil-immersed capacitor room, oil-immersed transformer room, oil-immersed reactor room, battery room, etc;
3, oil supply system - hydraulic station, lubricating oil storage, rolling oil system, centralized oil supply, system, oil storage room, oil pipe gallery, etc.;
4. Computer rooms - computer mainframe rooms, hard-software development and maintenance rooms, uninterruptible power supply rooms, buffer rooms, paper libraries, optical or magnetic recording material libraries, etc., in computing (information) centers, regionally managed computing stations, and computer rooms in the main production workshops.




